Game Summary
Dynamic Level Free Runner is a solo Unity parkour prototype with adaptive level design. It uses real-time Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment (DDA) to tailor challenges to player skill, maintaining flow, balanced difficulty, and engagement.
Responsibilities
Designed 3 levels
Concepted, Whiteboxed, User Tested Levels
Created all of the C# Scripts
Created a Adaptive Algorithm to change Level Design based on player performance and preference
Details
Team Size: 1 person (Solo Bachelor Project)
Genre: First-Person Action, Parkour
Setting: Dystopian City
Level Duration: 10 minutes
Role: Lead Level Designer, Programmer
Development Time: 10 Weeks
Engine: Unity Engine
Player Example Run
If you’re short on time, basically for this project I…
Created an adaptive algorithm that changes the level layout based on player performance
Created three levels, which serve the real-time adaptation, to teach, measure, and adapt
Created levels which feature multiple paths which cater to different player types
Wrote a 150-page bachelor’s thesis about real-time adaptation, possibilities, and issues
Organized weekly playtesting sessions to balance the strength of the adaptation process and player values
Programmed a parkour system, which features wall-running, ledge climbing and a boss level
Adaptive Gameplay System
Level 1– Teaching: Introduces core movement mechanics
(sprint, wallrun, slide, climb)
Level 2– Observation: Captures player metrics like completion
time, hesitation points, and success rate
Level 3– Adaptation: Dynamically restructures challenges based
on previous performance
Example: If a player excels at wall running but struggles with vaulting, the final level emphasizes wall run routes and gradually reintroduces vaults in safer contexts to support learning and flow.
Adaptive paths are generated in real time for different skill levels:
Advanced players: Complex,high-skill routes
Novice players: Simpler, forgiving alternatives
Prioritizes flow state through rhythm, momentum, and clarity
Minimal interruptions; no enemies, only traversal challenges
Designed to be engaging and non-frustrating, with clear
feedback loops
Flow-Centric Experience Design
Moodboard
Level 1 - Concept
Level 2 - Concept
Level 3 - Concept
Visual & Cognitive Design
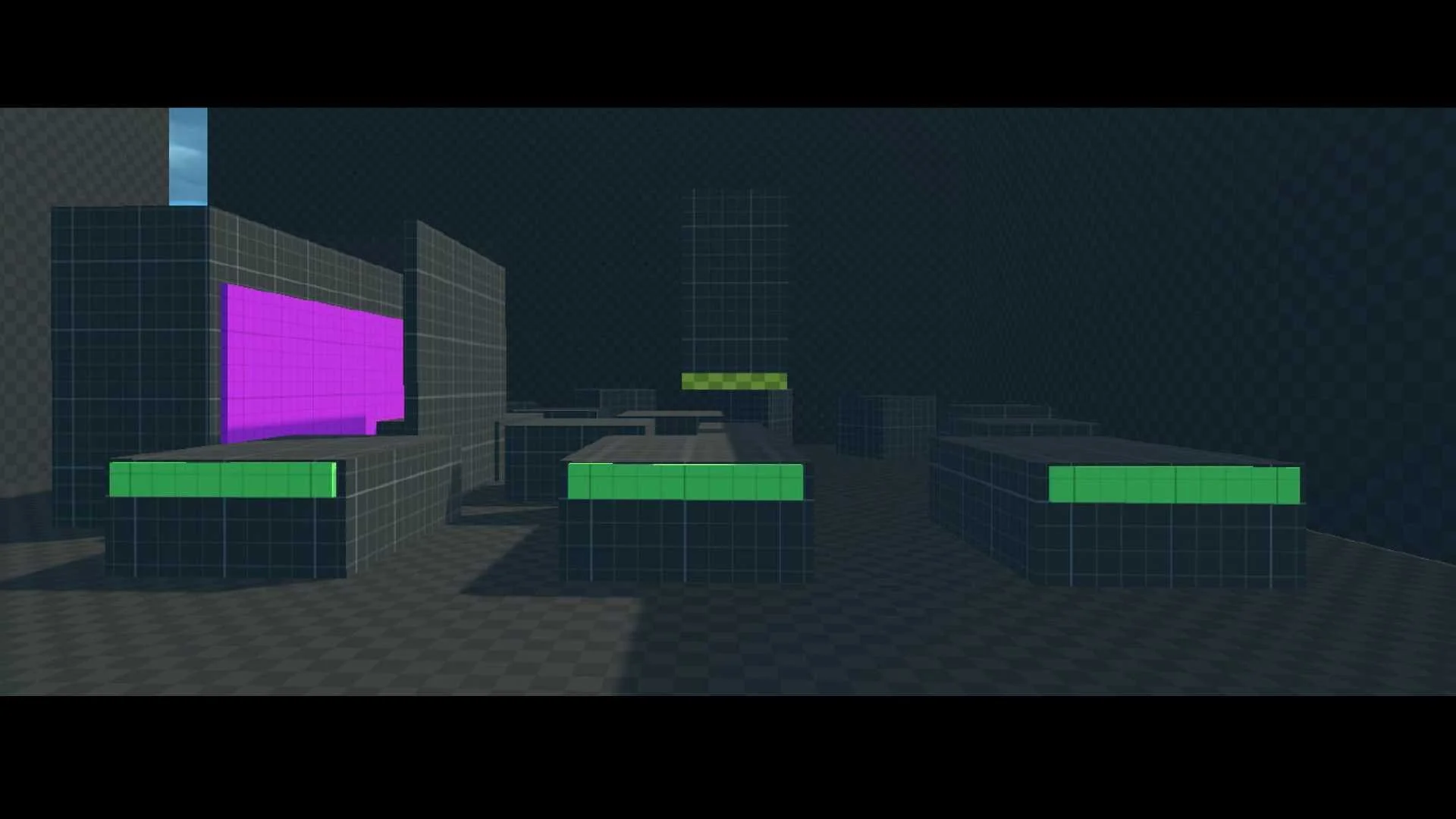
Minimalist Blockout Style: Grid and checkerboard visuals
highlight form and function
High contrast & clean readability: Supports fast reactions
and precise movement
Environmental storytelling via lighting, fog, and tone, no
text or cutscenes
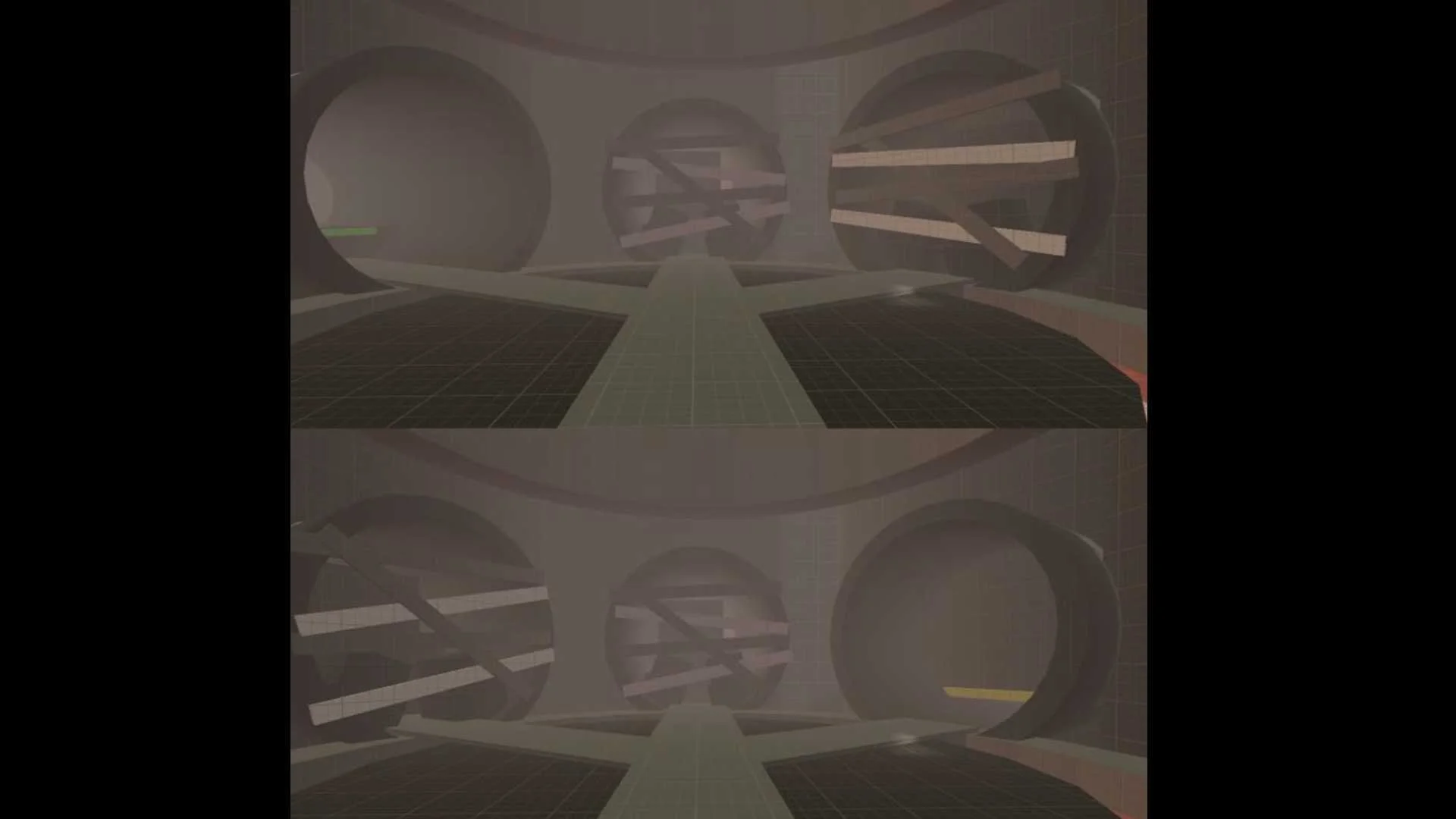
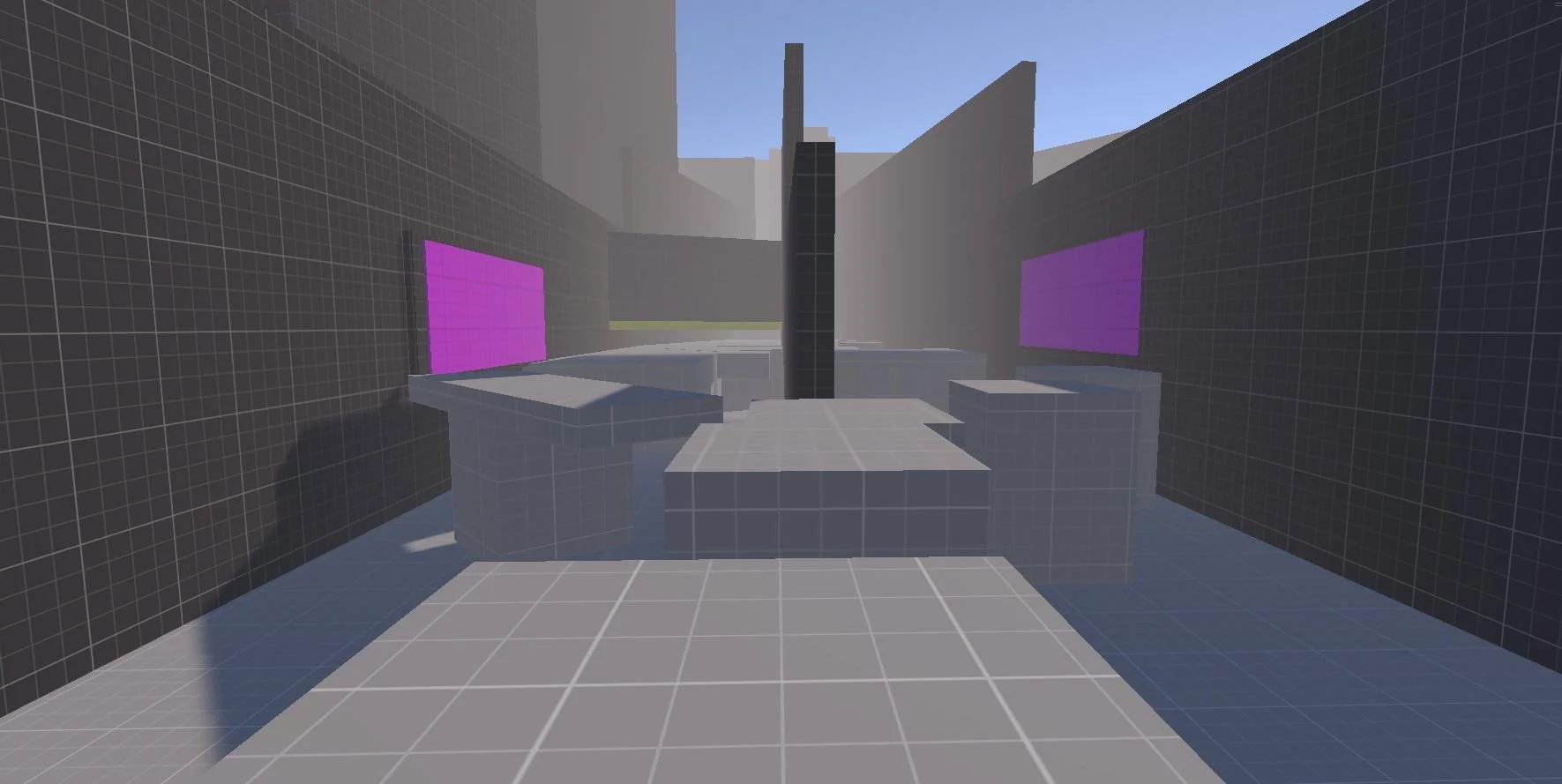
Color-coded traversal cues to eliminate intrusive tutorials:
Purple – Wall Running
Yellow – Sliding
Green – Climbing
Orange – Interactables/Checkpoints
Red – Hazards
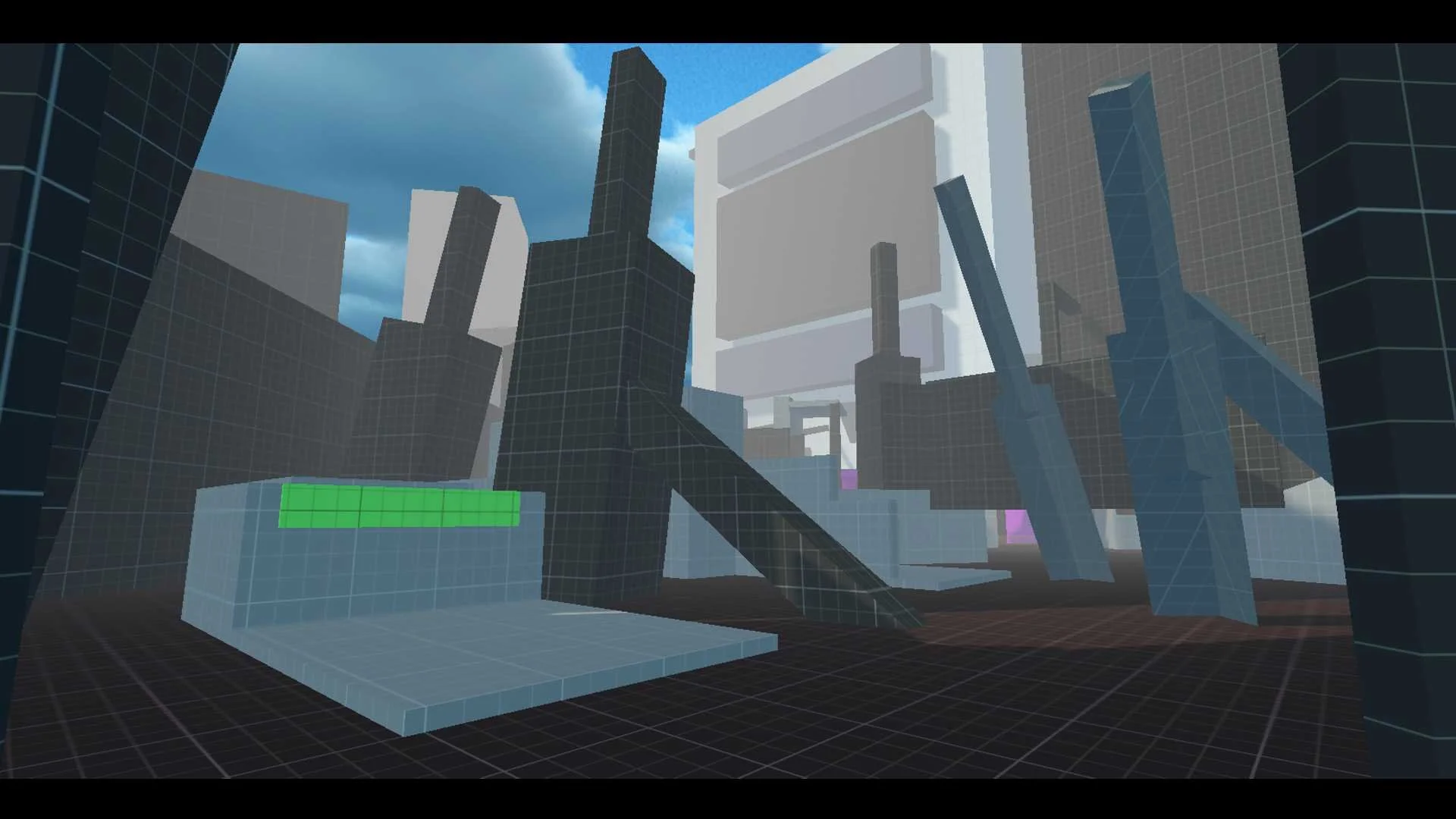
Setting & Atmosphere
Set in a toxic dystopian city, the game mirrors the player’s
journey through mood and architecture
Levels evolve from neutral on boarding environments to
emotionally charged, challenging spaces as the narrative and player skill progress
Wallrunning Surface
Sliding Indicator
Climbing Surface
Level 3 - Sewers
Testing & Results
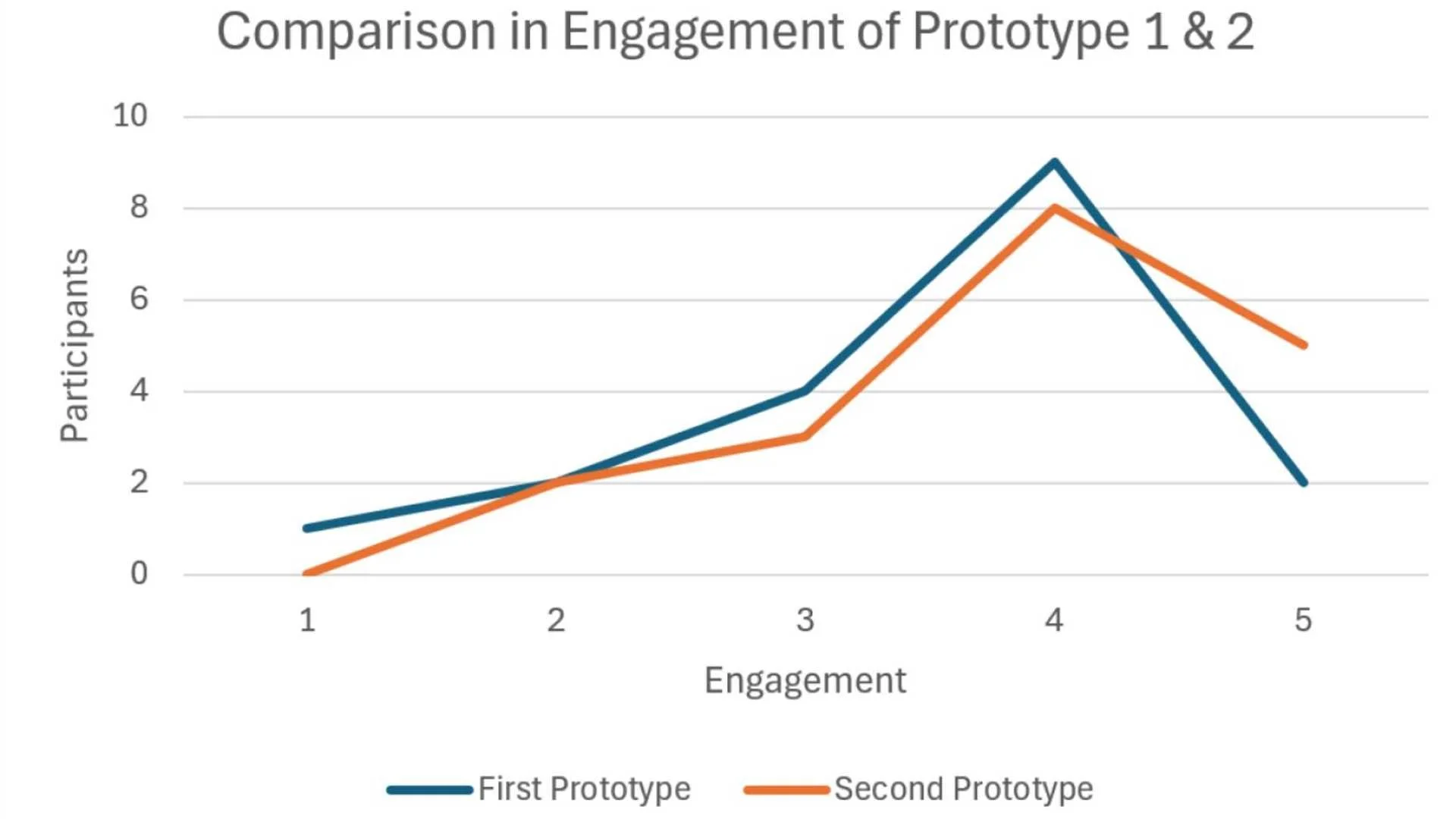
Static Prototype (Control) vs. Adaptive Prototype (DDA Enabled)
Measured Factors
Game Time Overall
Game Time in Segments
Player Fails
Player Sprint Duration
Player Traversal Preferences
Player Decisions
…
Findings
Adaptive version showed higher engagement, smoother skill
progression, and increased satisfaction
Players reported feeling more “in sync” with the game,
citing better rhythm and pacing
Design Philosophy
Flow-FirstGameplay: Every mechanic and layout choice
supports momentum, rhythm, and uninterrupted player movement.
Adaptive Challenge: Difficulty and pacing scale dynamically
based on player performance metrics like reaction time, hesitation, and success rate.
Player Agency & Expression: Multiple path options encourage
different playstyles and reinforce a sense of mastery and ownership.
Cognitive Simplicity: Color-coded affordances reduce cognitive
load and allow intuitive traversal without relying on tutorials.
Environmental Storytelling: Minimalist visuals paired with lighting,
fog, and progression-based atmosphere create narrative depth without text or cutscenes.
Form Follows Function: Blockout art and clean geometry emphasize
gameplay clarity, ensuring every surface communicates its use instantly.
Level 3 - Jumping Choices
Level 2 - Start
Result: Engagement Score (Blue: Static Prototype, Orange: Adaptation Prototype)
Level 3 - Adaptation in Player Choices
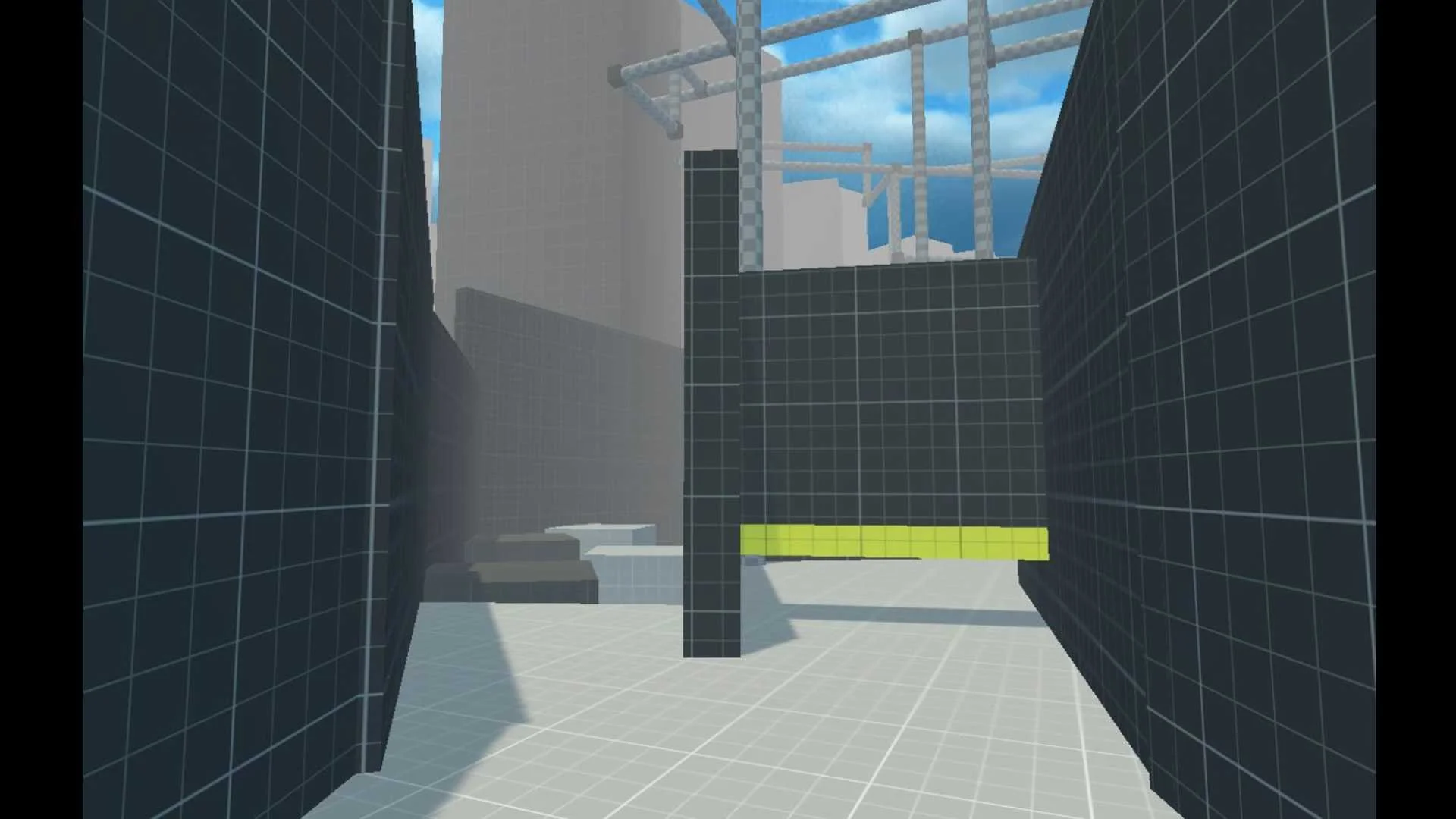
Level 1 - Tutorial Playground Area
Result: Changes player noticed
Forced Player Obstacles
Introduces every obstacle type, ensuring players experience each mechanic at least once.
Uses color-coded obstacles for intuitive recognition and quick learning.
Guarantees players make the connection between mechanics and visual cues before moving on.
Level 1 - Tutorial
The Playground
Open, low-pressure space for testing traversal mechanics (jumping, wall-running, gravity changes).
Lets players discover personal preferences and playstyles early.
Reinforces world rules (gravity, movement physics) through experimentation.
Learning in safe Environment
No fail states, ensuring confidence building and skill rehearsal without punishment.
Multiple routes encourage exploration and creative problem-solving.
Focus on player onboarding by blending freedom with subtle guidance.
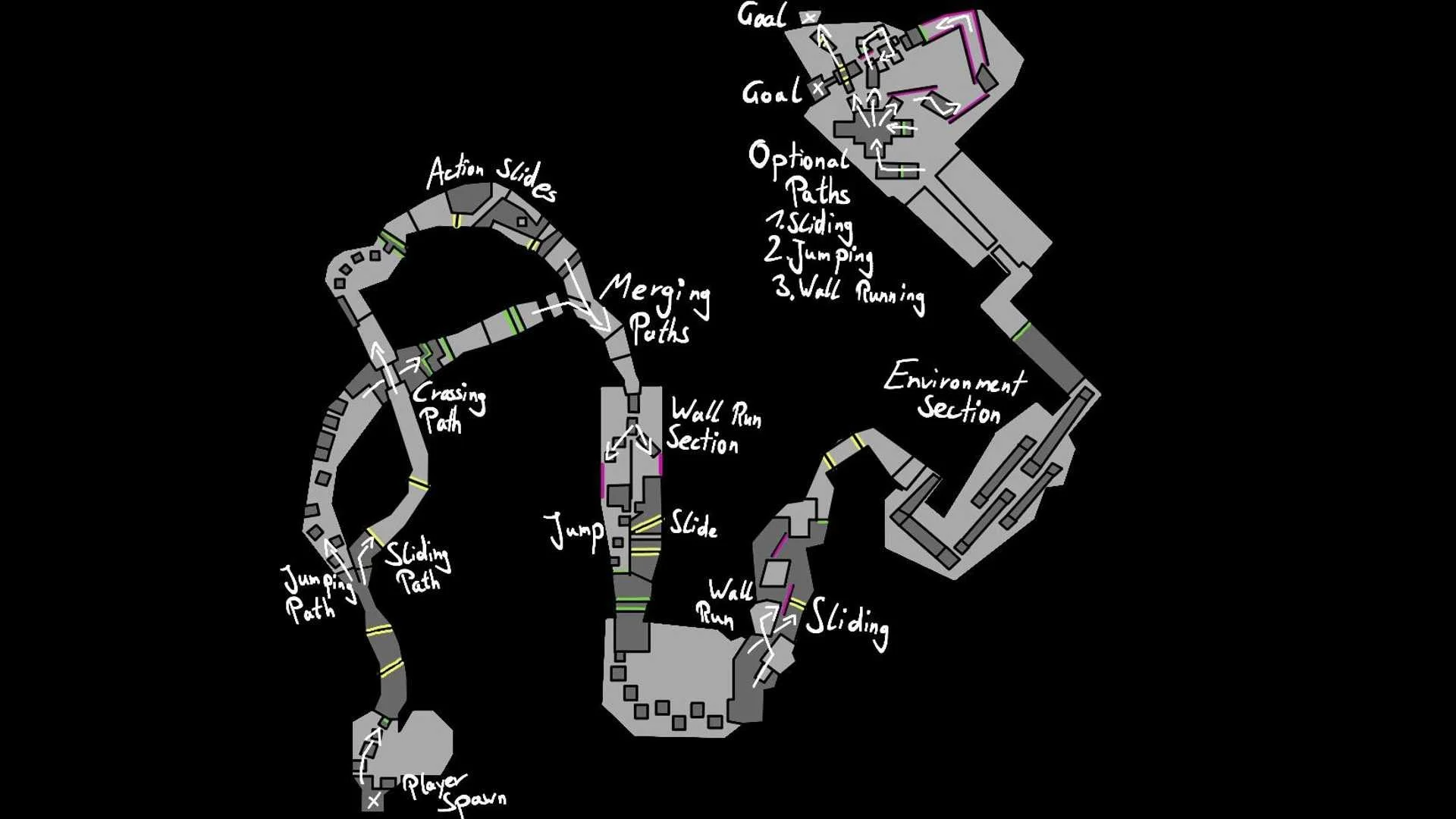
Level 2 - Measurements
Player Choices
Introduces fast, instinctive decision-making under light pressure.
Multiple choice points test player reaction without overcomplicating gameplay.
Keeps clear visual communication to maintain accessibility.
Linear Paths for Pacing
Alternates open choice sections with linear runs to prevent decision fatigue.
Uses linear paths for pacing control and environmental storytelling moments.
Environmental variety maintains engagement while teaching subtle traversal nuances.
Multi-Routes
Final area offers five distinct routes, collecting player preference data.
Each route caters to different playstyles (speed, precision, or exploration).
Data gathered here fuels personalized difficulty adjustments in the next level.
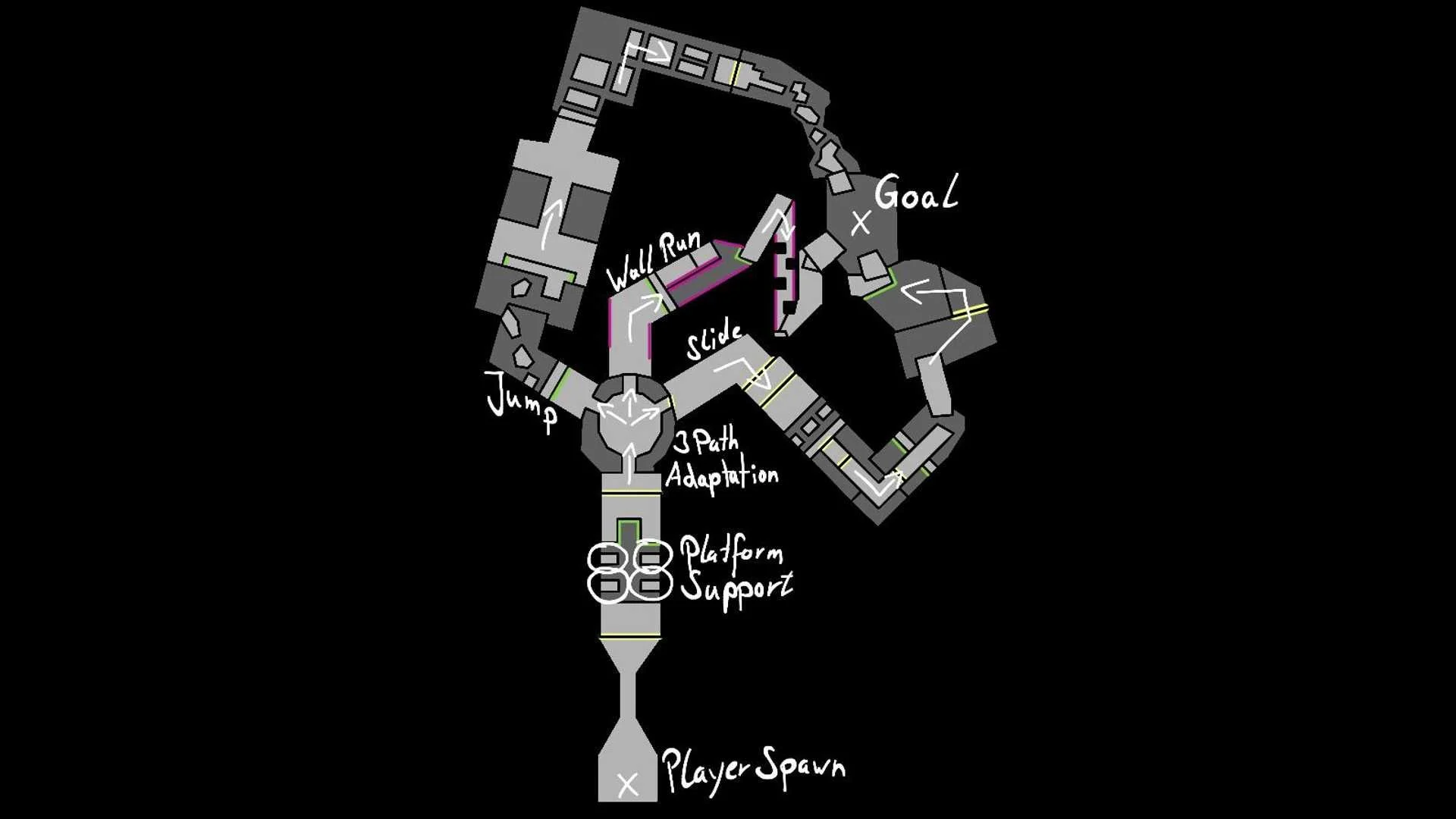
Level 3 - Adapted Level
Flow Support
Implements fail-safes like extra platforms to reduce unnecessary restarts.
Supports continuous momentum, preserving player immersion.
Reduces frustration by lowering repetitive failure points.
Player Preference Adaptation
Level layout and obstacles dynamically change based on Level 2’s data.
Adjustments include adding/removing paths, altering obstacle difficulty, and modifying traversal demands.
Creates individualized gameplay, increasing engagement and replayability.
Final Adapted Area
Three-path challenge where obstacles require the player’s strongest traversal method.
For wall-runners: wall-based obstacles; for jumpers: gap-jump challenges.
Acts as a final skill check, reinforcing mastery before game progression.
Issues, Iterations and Learnings
Sample Issues
Limited Player Choice
The level offered too few meaningful options for navigation. As a result, players felt constrained, and the adaptive system lacked sufficient data points to personalize the experience.
Sample Solutions
Expand Player Pathways
Introduced branching routes, optional challenges, and alternate traversal methods. This not only increases player agency but also generates richer data for the adaptive system to analyze player behavior.
Overly Simplistic Visuals
The environment was composed of basic shapes with little variation. Players reported that this reduced immersion and made the experience feel unfinished.
Enhance Environmental Design
Replaced placeholder shapes with more detailed assets, varied silhouettes, and contextual cues. Added environmental storytelling elements that have strengthened immersion while maintaining readability for gameplay.
Shallow Early Adaptation
In early stages of the development, the adaptive mechanics felt too simplistic. Players expected richer variations in difficulty and pacing without sacrificing their sense of agency.
Deepen Early Adaptation
Implemented a more layered difficulty scaling from the beginning of the level. Small but noticeable adjustments (e.g., obstacle timing, bonus opportunities) give players a sense of personalization early on while keeping core agency intact.
Learnings
Adaptive level design is very impactful, with visible and meaningful changes to keep players engaged.
Tutorials that introduce mechanics through “forced” obstacles with open areas afterwards, are effective for onboarding.
Playground spaces empower players to experiment without pressure and encourage mastery.
Artificial urgency can push spontaneous decision-making, but needs to feel natural.
Future adaptive systems should use many different metrics and meaningful make changes in traversal variety and comfort.
Player with Jumping Focus
Player with Wall Running Focus
More Screenshots